Gum Disease-1
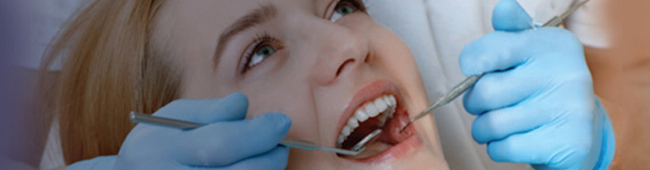
Gum disease is a very common condition and varies widely in severity where the gums around the teeth become swollen, sore or infected.
It is an infection of the tissues that surround and support your teeth and is most commonly a result of poor oral hygiene. It is a major cause of tooth loss in adults. Because gum disease is usually painless, you may not know you have it. If you have gum disease, your gums may bleed when you brush your teeth and you may have bad breath.
Our mouth is full of bacteria that combine with saliva to constantly form a sticky film known as plaque, which builds up on your teeth. When you consume food and drink high in carbohydrates (sugary or starchy foods), bacteria in plaque turn carbohydrates into the energy they need, producing acid at the same time. Over time, acid in plaque begins to break down your tooth’s surface and causes tooth decay.
Gum disease starts when food debris mixes with saliva and bacteria-forming plaque that sticks on the surfaces of teeth. Plaque is usually easy to remove by brushing and flossing your teeth. Plaque that is not removed can harden and can become mineralized and form a substance called Tartar or Calculus. Tartar sticks much more firmly to teeth than plaque and is very hard that brushing doesn’t clean and can only be removed by a professional dental cleaning. This bacterial growth of dental plaque and tartar is harmful for the health of the gums. The longer plaque and tartar are on teeth, the more harmful they become. If they are not removed from teeth, it builds up and they will begin to irritate the gums and can cause the gums to separate from the teeth. This can lead to redness with bleeding, inflammation and soreness. This early stage of inflammation of the gums caused by bacteria is known as Gingivitis. It is a mildest form of gum disease that can usually be reversed with daily brushing and flossing, and professional cleaning by a dentist. Although the gums may be irritated, the teeth are still firmly planted in their sockets. This form of gum disease does not include any loss of bone or tissue damage that hold teeth in place. At this stage the person should visit a dentist. Infact dental clinics in Delhi like ours ie ‘Smile Delhi-The Dental Clinic’ are making it a norm to remind their patients to come for a six monthly check and clean, as gum problems remain silent for a long time. General dentists in Delhi are able to treat this problem.
Other bacteria in plaque can also irritate your gums, making them inflamed and sore.
If left untreated, gingivitis will often extends from the gums to the bone. With time, plaque can spread and grow below the gum line and an advanced gum disease called Periodontitis (inflammation around the tooth) can develop. It is a serious disease that affects more tissues and structures and results in major damage to the soft tissues and bone, that support and surround the teeth which includes the gums, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone. Specialist dentists in Delhi , ie periodontists help treat this condition of periodontitis very proficiently. In our clinic the gum specialists have helped salvage some moving teeth also and increased their life.
If periodontitis is not treated, the underlying bone in the jaw below the gums gets damaged, inflamed or infected. Small spaces can open up between the gum and teeth and the gums start to recede or pull away from the teeth and form deep gum pockets. The body’s immune system fights the bacteria as the plaque spreads and grows below the gum line. These pockets collect plaque as they are very difficult to keep clean. Toxins produced by the bacteria in plaque irritate the gums and the body’s natural response to infection start to break down the bone and connective tissue that hold teeth in place. As the disease progresses into later stages, the pockets deepen and more gum tissue and bone tissue are destroyed. When this happens, teeth are no longer anchored in place, they may become loose and eventually fall out and may also lead to other health problems.
Gingivitis is not the same thing as periodontitis. Gingivitis (gum inflammation) usually precedes periodontitis (gum disease which has spread to the underlying bone from the gums). Although sometimes a person may be affected by both. Dentists in Delhi and dentists in India, have been providing quality gum treatment so not all gingivitis progresses to periodontitis
Whether your gum disease is stopped, slowed, or gets worse depends a great deal on how well you care for your teeth and gums every day.
Causes/Risk factors of gum disease?
Gum disease can be caused by a number of factors, but poor oral hygiene is the most common cause. Poor oral hygiene habits, infrequent or no dental care such as not brushing and flossing your teeth properly or on a daily basis, can cause plaque to build up on your teeth by allowing bacteria in plaque and calculus to remain on the teeth and infect the gums and thus make it easier for gingivitis to develop.
Plaque is the primary cause of gum disease.
But there are other factors that contribute to gum disease and can affect the health of your gums.
These include:
- Smoking or chewing tobacco– Tobacco use is linked with many serious illnesses such as cancer, lung disease and heart disease, as well as numerous other health problems Smoking or tobacco make it harder for gum tissue to repair or being able to heal. It is one of the most significant risk factors associated with the development and progression of gum disease. Additionally, smoking can lower the chances for successful treatment.
- Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy, puberty, menopause, and monthly menstruation, make gums more sensitive, which makes it easier for gingivitis to develop. The increase in hormones causes the blood vessels in the gums to be more susceptible to bacterial and chemical attack. At puberty, prevalence of gum disease ranges between 70%-90%.
- Illnesses may affect the condition of your gums- This includes diseases such as cancer or HIV that interfere with the immune system. Cancer and cancer treatment can make a person more susceptible to infection and increase the risk of gum disease. Systemic diseases- Diseases that interfere with the body’s inflammatory system may worsen the condition of the gums. These include cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis. Diabetes- a lifelong condition that causes a person’s blood sugar levels to become too high. Diabetes mellitus impairs circulation and the gums ability to heal. Because diabetes affects the body’s ability to use blood sugar, patients with this disease are at higher risk of developing infections, including gum disease and cavities.
- Genetic susceptibility or a family history of gum disease- Some people may be genetically susceptible to gum disease. Despite aggressive oral care habits, these people may be more likely to develop gum disease. Identifying these people with a genetic test before they even show signs of the disease and getting them into early intervention treatment may help them keep their teeth for a lifetime.
- Consuming certain medications (oral contraceptives, steroids, anti-epilepsy drugs, anti-depressants, calcium channel blockers, and cancer therapy drugs or chemotherapy) can affect oral health, because some lessen the flow of saliva, which has a protective effect on teeth and gums. Poor saliva production or without enough saliva, the mouth is vulnerable to infections such as gum disease. Anticonvulsant medications promote gum disease. Some medicines, such as the anticonvulsant drug, Dilantin and the anti-angina drugs, Procardia and Adalat, can cause abnormal overgrowth of gum tissue, this can make it difficult to keep teeth and gums clean.
- Compromised immunity (weakened immune system) because of conditions such as HIV and AIDS or certain other illness and their treatments, such as chemotherapy can also negatively affect gums, as can treatment of cancer.
- Poor nutrition /Obesity – A diet low in important nutrients can compromise the body’s immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infection such as vitamin C will impair healing. Also a diet high in sugar and carbohydrates and low in water intake, will increase the formation of plaque. Because gum disease begins as an infection, poor nutrition can worsen the condition of your gums. In addition, obesity may increase the risk of gum disease.
- Stress- Stress is linked to many serious conditions such as hypertension, cancer, and numerous other health problems. Stress impairs the body’s immune response to bacterial invasion and can make it more difficult for the body to fight off infection, including gum diseases.
- Age – gum disease becomes more common as you get older. Older people have the highest rates of gum disease
- Crooked, rotated, or overlapping teeth create more areas for plaque and calculus to accumulate and are harder to keep clean.
- Clenching or grinding teeth- This can put excess force on the supporting tissues of the teeth and could speed up the rate at which these gum tissues are destroyed.
- Alcohol affects oral defense mechanisms.
- Mouth breathing can be harsh on the gums when they aren’t protected by the lips, causing chronic irritation and inflammation.
- Dental appliances that fit poorly
- Broken fillings
Warning signs or symptoms
Gum disease may progress painlessly, producing few obvious signs, even in the late stages of the disease. Although the symptoms of periodontal disease often are subtle, the condition is not entirely without warning signs. Sometimes patients have come to us for some other dental treatment and the dentists in our clinic have pointed out the gum disease they are suffering from. Dentists in dental clinics in Delhi and in Dental Clinics in India have helped patients in the diagnosis of some systemic problems like diabetes due to the symptoms their gums may be showing. A person with gingivitis will typically have one or more of the following signs and symptoms-
- Gums that are red, tender, or swollen
- Gums that bleed when you brush or floss your teeth
- Formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums that trap food, plaque and debris.
- Sensitive teeth
- Gums that look like they have pulled away from the teeth(root of the tooth becomes uncovered by the shrinking, diseased gums), causing the teeth to look longer than before
- Permanent teeth lose gum tissue or bone around the teeth and the teeth may separate, become loose or fall out
- Any change in the way the teeth fit together when you bite (malocclusion) or spaces opening up between teeth
- White spots or plaques on the gums
- Pus between teeth and gums
- Sores in your mouth
- Pain when chewing or while eating hard food
- Any change in the fit of partial dentures
- Foul-smelling breath or bad taste in the mouth that does not go away after you brush your teeth
Dentists in both dental clinics in Delhi and dental clinics in India , are
1- Helping to educate patients about gum disease to prevent onset
2- Treating the already established gum diseases
Thus the life span of natural teeth has increased.
Posted By – Dr. Shriya